Table of Contents

Narrowband Filters: Unveiling the Hidden Universe in Astrophotography
Understanding Narrowband Filters:
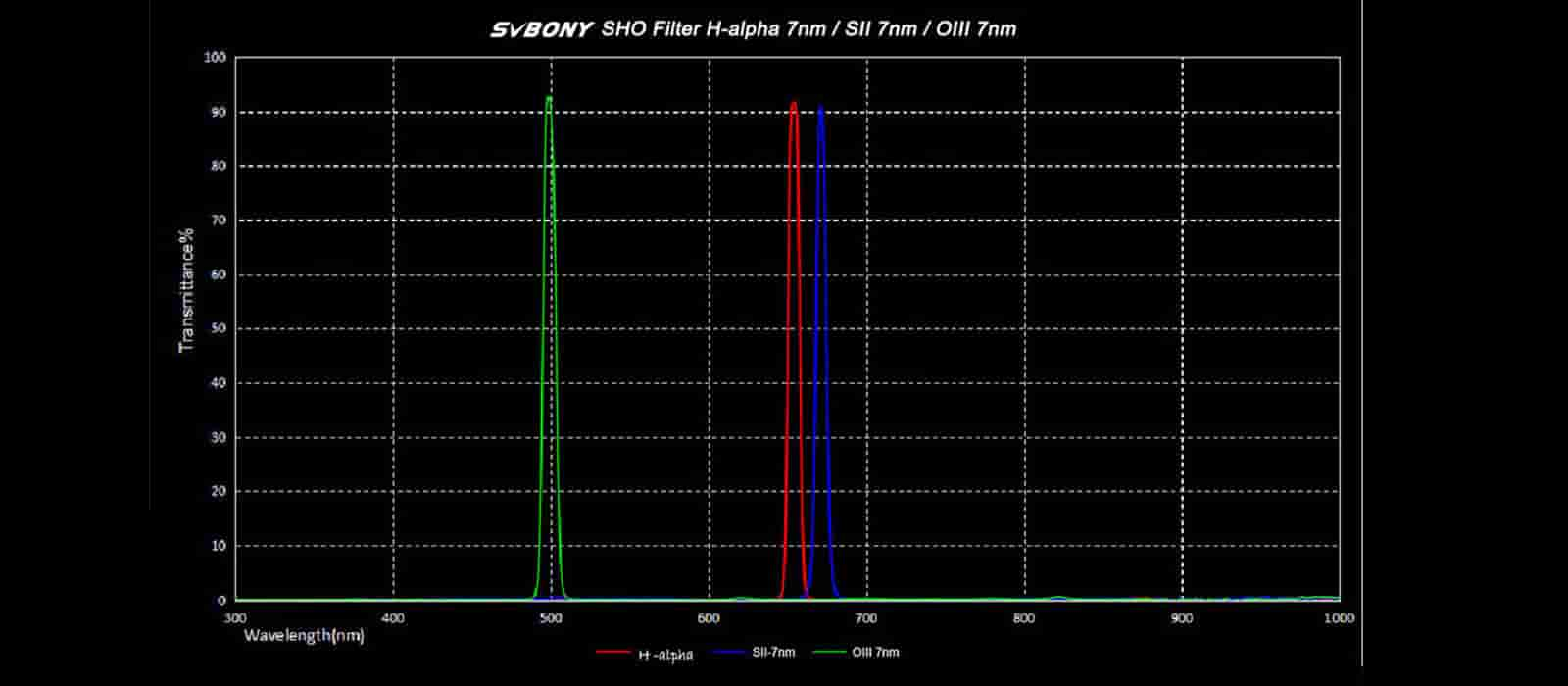
Narrowband filters are optical filters that selectively transmit specific wavelengths of light while blocking out others. Unlike broad-spectrum filters used in regular photography, narrowband filters isolate narrow regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The most commonly used narrowband filters in astrophotography include hydrogen-alpha (Ha), oxygen III (OIII), and sulfur II (SII) filters.
Benefits of Narrowband Filters:
Light Pollution Mitigation: Narrowband filters are exceptionally effective at reducing the impact of light pollution, allowing astrophotographers to capture breathtaking images even from heavily light-polluted areas. By isolating specific wavelengths emitted by nebulae and other deep-sky objects, narrowband filters help reveal the intricate details that would otherwise be obscured by unwanted light sources.
Enhanced Contrast: By capturing only the light emitted by specific elements, narrowband filters offer high contrast images. This enables astrophotographers to emphasize particular features or structures within an object, resulting in striking and visually captivating photographs.
Longer Exposure Times: Narrowband filters capture a narrower range of wavelengths, which means longer exposure times are required to gather sufficient light. However, this extended exposure time allows the filters to capture more detail and unveil faint structures that would otherwise remain hidden.
Versatility: Narrowband filters can be used with both monochrome and color cameras. For monochrome cameras, individual filters can be used in combination to create stunning narrowband images. Color cameras can benefit from one-shot color (OSC) narrowband filters, which capture multiple narrowband wavelengths simultaneously through a single exposure.

Tips for Using Narrowband Filters:
Planning is Key: Research and identify celestial objects that emit strong hydrogen-alpha, oxygen III, or sulfur II emissions. Understanding the specific wavelengths emitted by your target objects will help you determine which filters are best suited for capturing their unique features.
Patience and Persistence: Due to the longer exposure times required with narrowband imaging, patience is essential. It may take several hours of cumulative exposure time to gather enough data for a high-quality image. Persisting through multiple imaging sessions can yield remarkable results.
Post-processing Expertise: Processing narrowband images requires specialized knowledge and techniques. Software such as PixInsight or Adobe Photoshop can aid in extracting intricate details and enhancing the final image's visual impact.
Conclusion:
Narrowband filters open up a whole new dimension of astrophotography, allowing us to explore and reveal hidden features of the universe. By selectively isolating specific wavelengths of light, these filters mitigate the challenges posed by light pollution, enhance contrast, and reveal details that would otherwise remain unseen. Incorporating narrowband filters into your astrophotography toolkit can unlock breathtaking images and provide a deeper understanding of the cosmos.
Whether you're a seasoned astrophotographer or just starting your journey, narrowband filters offer an invaluable tool to capture the wonders of the universe in all their glory. Embrace the possibilities and immerse yourself in the fascinating world of narrowband astrophotography filters.

There are no customer reviews yet . Leave a Reply !